Delta Exposure and Portfolio Risk | A Practical Guide to Traders
- Jul 1, 2025
- 4 min read

When derivatives and active trading are involved, it is crucial to realise how your portfolio will respond to market fluctuations. Traders refer to the Greeks a lot, and the most basic among them is delta. Yet, behind its popularity, several traders misinterpret its deeper meaning or simply do not apply it efficiently, which hinders their ability to control risk.
The present blog is a handy reference to learn about delta exposure, how delta impacts portfolio risk, an example of delta portfolio risk, and how to think about portfolio hedging with options and how to handle delta risk in a portfolio.
What is Delta Exposure Meaning - The Foundation
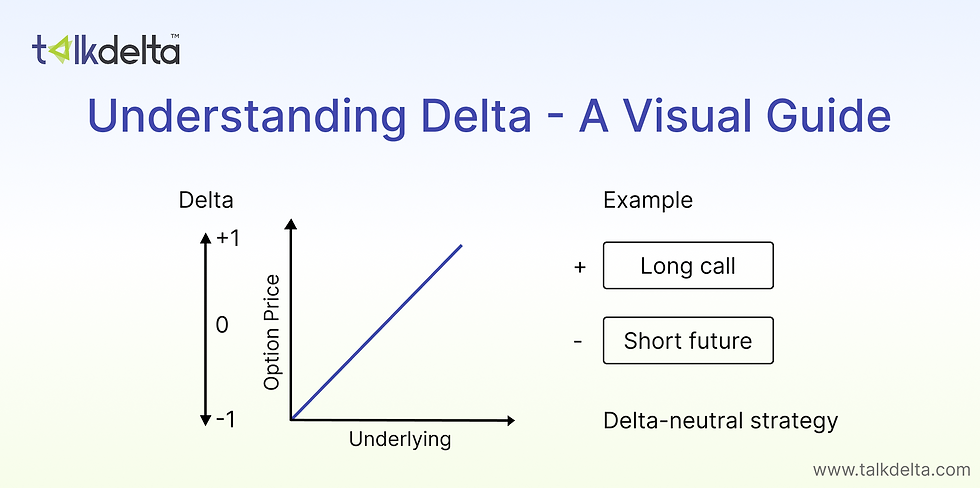
Delta, in its essence, is the rate of change of the price of an option with regard to a 1 ₹ change in the underlying asset. Suppose a NIFTY call option has a delta of 0.5; it means that the option will gain ₹0.50 on every ₹1 increase in the NIFTY index.
But the meaning of delta exposure extends beyond single contracts. It is the sum of the directional sensitivity of your whole portfolio to changes in the underlying assets. A portfolio with a net delta of +500 is effectively exposed like 500 shares (or equivalent units) of the underlying. A 1-point shift of NIFTY upwards would result in a 500-rupee gain in your portfolio theoretically.
Interpreting Delta
Delta = 0: Market-neutral: minimum exposure
Bullish exposure: Positive Delta
Negative Delta: Bearish exposure
The Impact of Delta on Portfolio Risk
One of the direct directional risk measures is delta exposure. Huge delta exposure, particularly unhedged, can produce huge profits or losses with even minor market fluctuations.
The major methods through which Delta influences Portfolio Risk include:
Direction Sensitivity of the Market:
A highly positive delta portfolio is susceptible to market declines.
A high negative delta portfolio loses during market rallies.
Volatility-Driven Delta Drift:
Hidden risks: Delta can change (because of gamma) without large moves in the underlying.
In turbulent markets, this change in delta (delta drift) contributes to uncertainty.
Position Size and Leverage:
A trader may believe he is safe having a small amount of contracts, only to find out that a delta-heavy portfolio, specifically leveraged portfolios, increases exposure and risk.
Inconsistent Delta Between Positions:
Delta tracking is important when you have several positions (calls, puts, spreads) in various assets.
A single bear stock option would compensate a bullish index position.
Delta exposure is to know the temperature of your portfolio; it does not explain everything, but it will tell you when it is too hot or too cold.
Portfolio Hedging with Options - The Delta-Based Description
The best option-based approach to portfolio hedging is delta balancing - changing your positions to make the net delta approach zero.

Popular Delta Hedging Strategies:
A. Buying/Selling Options:
Downside exposure can be neutralised by adding puts to a long delta portfolio.
Delta can also be reduced by selling calls (and introducing new risk).
B. Futures Hedging:
A pure method of directional hedge is to add NIFTY or stock futures in the direction opposite to your net delta.
C. Ratio Spreads:
To hedge delta and net exposure at controlled cost, traders will use spreads such as ratio calls or put spreads.
D. Dynamic Hedging:
It is affected by continuously rolling hedges as the delta changes during the day.
In India, algorithm-driven systems to automate this task are already available.
Example:
Suppose your portfolio net delta is +400, and the delta of each NIFTY futures is +100, then you may sell 4 NIFTY futures to make the portfolio directionally neutral.
How to Handle Delta Risk in Portfolio
Effective management of the delta risk of a portfolio does not imply removing delta. Rather, it is the knowledge of when and how much delta to be carried depending on market perception, volatility and capital.
A. Familiarise Yourself with Delta Profile
A platform or spreadsheet should be used to track the delta of every position.
Monitor net delta changes (net delta) on a day-to-day basis, particularly when you are actively trading options.
B. Segmented Delta Observance
Decompose your delta by sector (e.g., financials, IT) or by type (index vs stock-specific).
This will prevent inconspicuous clustering of directional risk.
C. Combine Greeks
Delta does not act singularly. Keep an eye on gamma (delta change), vega (IV sensitivity) and theta (time decay).
The sudden change in delta can be brought about by a high gamma position.
D. Delta Tolerance Zones
Establish reasonable ranges of delta exposure relative to your capital and plan (ex: +/-100 on conservative portfolios).
E. Scenario Analysis
Simulate various market movements and observe what your portfolio delta will do.
Real-time simulators (also called What-If simulators) are becoming available on many platforms.
Delta Exposure Tracking and Management Tools
In 2025, the traders are fortunate to have smart tools that accomplish complicated delta analysis easily.
Tools:
TalkOptions (India-based) - Net delta views, spread builders, IV overlays.
Algo IQ Delta Manager – Provides rule-based delta balancing and support of broker APIs.
Broker Tools (Fyers, Trademart, Upstock) – Basic Greeks tracking is provided in premium versions.
Certain brokers provide delta-linked margin calculators as well, which allow you to optimise capital usage given delta neutrality.
Delta in Strategy Design: More Than a Risk Metric
Delta is a metric that goes beyond a measure of risk; it is a strategy enabler.

Famous Delta Built Strategies:
Delta-Neutral Straddles/Strangles- Suitable in high volatility events.
Directional Spreads where Delta is defined- E.g., Bull Call Spread where delta on entry is 0.6.
Delta-Gamma Scalp- Experienced traders employ gamma-laden positions to make money via scalping the delta changes within the day.
Knowing delta allows you to structure your trades the way you want them to be, based on your market opinion, time frame and risk tolerance.
The Final Word
Delta is not an option in contemporary options trading. Trading index futures, writing options or designing complex spreads, learning about delta exposure, its behavioural characteristics and the ways to modify it is the ticket to long-term trading survival.


Whenever I think of premium winter jackets, the Wellensteyn Jacke Herren comes to mind first. It’s made for men who value comfort and style equally. The jacket protects against wind and rain while still being breathable. I feel confident wearing it anywhere, whether at work, while traveling, or casually.
The Wellensteyn Jacke Damen is worth every penny. Unlike cheaper jackets, this one lasts much longer and still looks elegant after months of use. I appreciate that it’s both breathable and warm, which is rare to find. It has truly elevated my winter wardrobe to the next level.
Safeguarding the Future of African Grey Parrots: Conservation Challenges and Pathways Forward
By Jimmy Jones, Avian Enthusiast and Contributor at ExoticAfricanGrey.uk
In the lush rainforests of Central and West Africa, where the canopy whispers secrets of ancient ecosystems, the African Grey Parrot (Psittacus erithacus) dances on the edge of extinction. These remarkable birds, with their silver-grey plumage, crimson tails, and uncanny intelligence, have captivated humans for centuries. Yet, today, they stand as a poignant symbol of the broader crisis in bird conservation: habitat loss, illegal wildlife trade, and the relentless march of climate change. As a global partnership like BirdLife International continues to champion biodiversity protection, it's imperative we shine a light on species like the African Grey—Endangered on the…
<ul>
<li><a href="https://buyrealdocument.com/product/australian-id-card/">Where to get an ID card</a></li>
<li><a href="https://buyrealdocument.com/product/canadian-id-card/">Get an identification card</a></li>
<li><a href="https://buyrealdocument.com/product/maryland-id-card/">Where to go for an identification card</a></li>
<li><a href="https://buyrealdocument.com/product/australian-id-card/">Where to get an ID</a></li>
<li><a href="https://buyrealdocument.com/product/canadian-id-card/">How to get an identification card</a></li>
<li><a href="https://buyrealdocument.com/product/maryland-id-card/">Apply for an ID card online</a></li>
<li><a href="https://buyrealdocument.com/product/australian-id-card/">How to get a new ID</a></li>
<li><a href="https://buyrealdocument.com/product/canadian-id-card/">Order a new ID card</a></li>
<li><a href="https://buyrealdocument.com/product/canadian-drivers-license/">Get a new driver’s license</a></li>
<li><a href="https://buyrealdocument.com/product/buy-california-driving-license/">Documents needed for a REAL ID</a></li>
<li><a href="https://buyrealdocument.com/product/buy-california-driving-license/">What is a REAL ID?</a></li>
<li><a href="https://buyrealdocument.com/product/canadian-id-card/">ID cards in Canada</a></li>
<li><a href="https://buyrealdocument.com/product/buy-california-driving-license/">What does a REAL ID look like?</a></li>
<li><a href="https://buyrealdocument.com/product/maryland-id-card/">Order an identification card online</a></li>
<li><a href="https://buyrealdocument.com/product/australian-passport-online/">Passport card vs. REAL ID</a></li>
<li><a href="https://buyrealdocument.com/product/canadian-id-card/">How to get a new identification card</a></li>
<li><a href="https://buyrealdocument.com/product/buy-california-driving-license/">REAL ID driver’s license requirements</a></li>
<li><a href="https://buyrealdocument.com/product/australian-id-card/">Order ID online</a></li>
<li><a href="https://buyrealdocument.com/product/maryland-id-card/">Order ID …
The Ultimate Guide to Amazonian Cubensis
Looking into exotic mushroom strains? you’ve likely heard about the legendary Amazonian Cubensis. Amazonian cubensis mushrooms are well known in the shroom growing community for their dense caps and thick stems. Users have noted effects that are deeply introspective and often more vivid than common cubensis strains. ⤵️
https://hempdelics.com/product/amazonian-cubensis/